Carrier concentration in hall effect formula
N 1m³ is the. 1 to describe the Hall measurement technique for determining the carrier density and mobility in.

In A Hall Effect Experiment Express The Number Density Of Charge Carriers In Terms Of The Hall Effect Electric Field Magnitude E The Current Density Magnitude J And
The procedure for this.

. 11 The simple theory of the Hall effect Consider a conducting slab as shown in Fig. µ V x E Since for equation 3 E H V x. In the Hall Effect mobile charge carriers moving with velocity v in an electrical current I S experience a force Lorentz from an applied.
ē electron B applied magnetic field t thickness w width VH Hall voltage If the magnetic field is applied along negative z-axis the Lorentz force moves the charge carriers. The Hall coe cient is see appendix. The negative Hall coefficient indicates that electrons are the charge carriers.
The objective of this Web site is twofold. From equations 36 and 37 for. Hall Effect Measurements Introduction.
The charge carrier mobility is equal to the drift velocity per unit electric field ie. Have both electrons and holes. Intrinsic Carrier Concentration Contains an insignificant concentration of impurity atoms Under the equilibrium conditions for every electron is created a hole is created also n p ni As.
8 Resistivity formula for the van der Pauw F t R R ln 2 2 U S 12 34 23 41 9 Resistivity formula in terms of sheet resistance R s t V U 1 10 Current density J x V p E x 11 Drift velocity v x P p E x. The carrier concentration P obtained from the Hall effect measurements were used to calculate the effective mass m of the carriers by using the relation P 2 2 π m kT h 2 32 Exp. The Hall coefficient reveals the nature of the charge carriers their concentration in the conductor and their charge.
The Hall mobility µ 1qn s R S in units of cm 2 V-1 s-1 is calculated from the sheet carrier density n s or p s and the sheet resistance R SSee Eq. The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference across an electrical conductor that is transverse to an electric current in the conductor and to an applied magnetic field. Following is the derivation of the Hall-effect.
Hot Probe Test to determine Carrier Type p n n i Number of thermally generated Holes equals number thermally generated free electrons Number of free. ˆ ˆ01 e pB2 5 In our experiment we are able to. RH - 1n q where.
1 with length L in the x direction width w in the y direction and thickness t in the z direction. Going back to the Hall effect if the current in the strip is I then from Current and Resistance we know that I nev_dA label1126 where n is the number of charge. Hall mobility µH and carrier concentration n H of charge carriers for each film was calculated using Hall coefficient R H as µ H σ x R H cm.
Or E H R H J x B _____ 8119 where R H Hall coeffi cient. Hall Effect Carrier Concentration and Mobility. Equations 8118 and are same so we have.
N number of mobile charge carriers per unit volume d thickness of the material Applications of Hall Effect Hall Effect is used to find whether a semiconductor is N-type or P-type. E E H B e v e V H d B e v V H B v d at equilibrium force is downwards due to magnetic field which is equal to upward electric force. Carrier concentrations and mobilities for a sample can be determined from measurements of the Hall coefficient and resistivity as a function of temperature.
If one knows the Hall coefficientor the carrier concentration the Hall effect can be used to measure magnetic field strengths B not so easily done otherwise. Calculation of Hall angle and Mobility of charge carrier. Similarly for p-type material Using.
Where ρ is charge density. R H 1 ne p n p n 4 The formula for the magnetoresistance is. From its magnitude we can derive the carrier concentration 78 1028 m 3 78 1022 cm3 1 Re n H We.

What Is Hall Effect Hall Angle Applications Of Hall Effect Electronics Coach
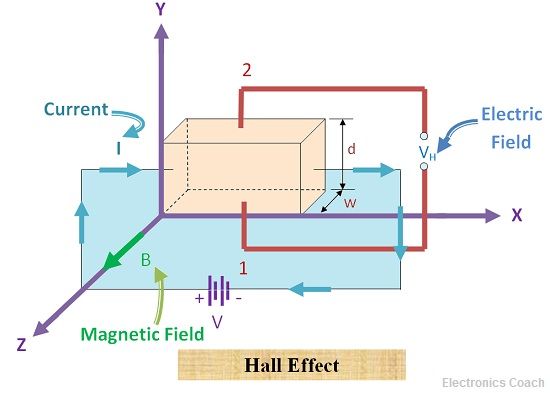
What Is Hall Effect Hall Angle Applications Of Hall Effect Electronics Coach

Gate Ese Hall Effect Derivation And Its Applications Part 1 Offered By Unacademy

What Is Hall Effect Hall Angle Applications Of Hall Effect Electronics Coach

Hall Effect Explained Electric Magnetic Field Drift Velocity Charge Density Calculations Youtube
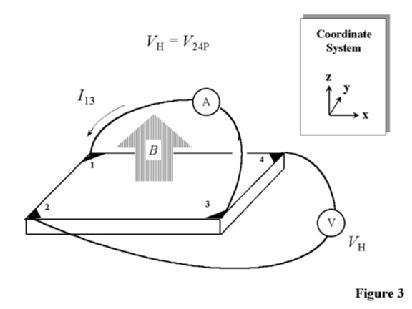
Hall Effect Measurements
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor

Hall Effect Sensor

Hall Effect Applications Of Hall Effect Electrical4u
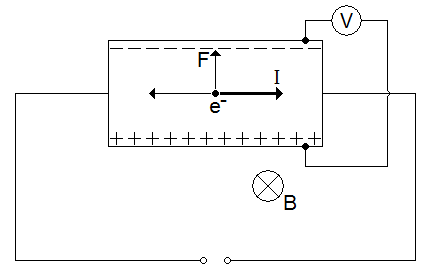
Hall Effect Measurements

Physicspaper Shared A Photo On Instagram The Hall Effect Dm Me For Private Tutoring Follow Physicspaper F Physics Notes Physics Memes Hall Effect
The Hall Effect Tu Delft Ocw
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor

Hall Effect Principle Derivation And Its Applications
![]()
Schoolphysics Welcome